Potential Difference










Potential Difference
Electric Potential:
Electric potential at a point in electric field is defined to be equal to the minimum work done by an external agent in moving a unit positive charge from infinity or a reference point to that point against the electrical force of the field. If W is the work done by external agent in bringing a positive test charge qo from infinity to a point then the potential V at that point,
According to Newtons Third Law of motion i.e. for every action there is equal and opposite reaction
The work done by an external agent in bringing a positive test charge qo from infinity to a point will be equal and opposite ti the work done by the electric field on a positive test charge qo, if
The SI unit of electric potential is joule/coulomb or volt.
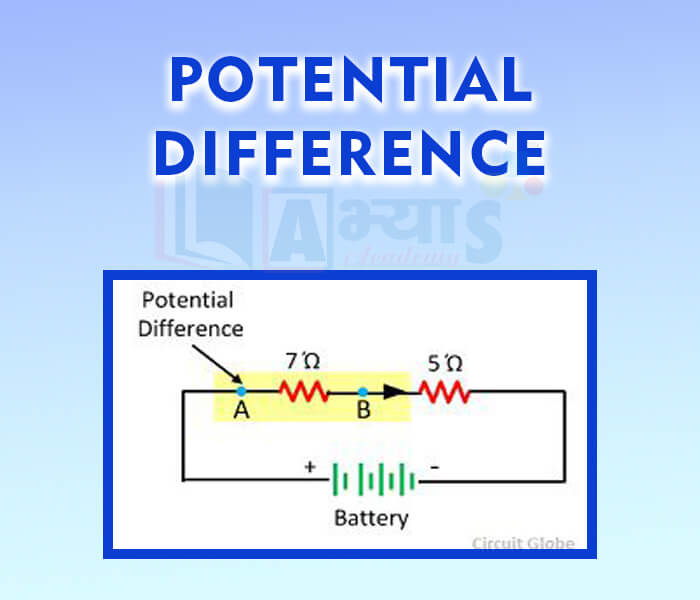
Potential Difference: Potential difference between two points is equal to the minimum work done in moving a unit positive test charge from one point to the other.
,
is the work done by the electric field then
Hence the work done by external agent
And Work done by the electric field is
We know that heat energy flows from the higher temperature to the lower temperature, and this process stops when the both are at the same temperature. Same is the case with electricity, when the ends of an electrical conductor are at different potentials or we can say that when there is a potential difference - charge in the conductor flow from the higher potential to the lower potential.The flow of charge persists until both ends reach the same potential. Without a potential difference, no flow of charge will take place.
Illustration: How much work is done in moving a charge of 2 C from a point of 118 V to a point at 128 V ?
Solution: Given, charge, q = 2 C
Potential at point A
and Potential at point B
Work done, W = ? We know that,
Potential difference,
Work Done,
So, the work done in moving the charge is 20 J.
When a potential difference is applied across the ends of a linear - metallic conductor: _________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation |
Which of the following statements are true? 1. During electrolysis charge does not flows through electrolyte solution via electrons. 2. The randomly moving electrons in a metal wire will start moving in a potential difference is applied across it. 3. A negatively charged particle has higher electric potential than a positively charged particle. 4. Charge flows only through negative charge carriers like electrons | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation |
A suitable unit for expressing electric field strength is __________________ | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.
